Population Attributes
Population Attributes: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Population, Population versus Species, Population Attributes, Birth Rate, Death Rate, Age Structure, Population Dispersal, Sex Ratio, Population Growth, Population Growth Curve, etc.
Important Questions on Population Attributes
Essential information that can be obtained by studying the population density of an organism is,
Which of the following variable is not involved in the exponential growth curve?
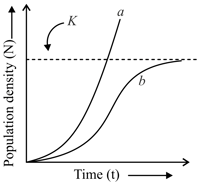
In the population growth curves shown below, ‘a’ and ‘b’ is representing:
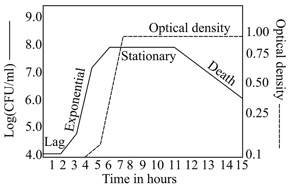
When a of Escherichia coli culture is grown at under laboratory conditions, the population of cells exhibits four distinct phases (Figure): (i) lag phase, wherein cells adapt to the environment, (ii) exponential phase, wherein cells undergo rapid division, and the population keeps doubling, (iii) stationary phase, wherein the rate of cell division decreases, and some cells begin to die, (iv) death phase commences (much before cell lysis), wherein the rate of cell death exceeds the rate of cell division. The two curves in the graph indicate the methods used to measure growth, viz. turbidity method (optical density) and counting colonies on a solid nutrient medium, wherein each live cell grows into an individual colony termed as a colony-forming unit (CFU). The death phase remains constant in the turbidity method even though the number of live bacteria decreases, because
Consider that plant species is more efficient than plant species in nutrient uptake, but plant is a better seed disperser. In this example, the resource under competition is nutrient; but, nutrient acquisition is related to availability. If a disturbance opens up new space for colonization, plant is expected to arrive first and maintain its presence in the community until plant arrives and begins competing with plant . Eventually, plant will outcompete plant because plant is more efficient in nutrient acquisition and grows faster. With an increasing plant population, the plant population will decline, and given enough time, has a possibility of shrinking in number in the present habitat. The way(s) of preventing the declining numbers of plant could be
You are provided with a bacterial culture (generation time of 30 minutes) in the exponential (logarithmic) growth phase. You transferred an aliquot of this culture to a fresh medium, which now contains cells/milliliter. Considering that this culture does not exhibit a lag phase, and growth conditions remain unchanged, the cells/millilitre that you would obtain after hours of incubation is
Life history variation is related to
The following plots represent the body size distributions of a fruit fly population. Dashed lines represent the ancestral distributions and continuous lines represent the distributions after a few generations. If the larger individuals have better survival as well as higher reproductive rates, which diagram below best represents the expected change in the distribution of body size (-axis represents body size while Y-axis represents frequency)
Which of the following deals with the interaction of populations with their environment?
Which branch of ecology deals with the study of changes in population sizes (population dynamics) over a period of time ?
Which of the following growth curves represents growth of bacteria in a culture medium that contains both glucose and lactose?
Under which of the following conditions is Semelparous reproduction (where organisms produces all its offspring in a single reproductive event) is most likely to be favoured?
Which of the following life history adaptations is least likely when predation pressure, on a fish species that grows in size continuously throughout its lifespan, is concentrated on the larger individuals?
Permanent outward movement of individuals is called
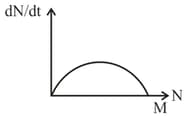
In the graph below, where is population size and is time, represents
Species with high fecundity, high growth rates, and small body sizes are typically
According to the logistic population growth model, the growth rate is independent of
If 4 individuals are died and 8 individuals are born in a laboratory population of 40 fruit flies during time interval of 7 days, calculate the intrinsic rate of natural increase for fruit fly population per week
The density of the population will increase when:
